Generate NHibernate Classes and Mapping with Ease
NHibernate is a widely used ORM solution for Microsoft .NET - it helps mapping .NET classes to database tables and creating a data access layer with little effort. NHibernate Generator approach supposes generating NHibernate entity code and NHibernate mapping based on an existing database schema. This approach is rather popular and there is a number of tools implementing it.
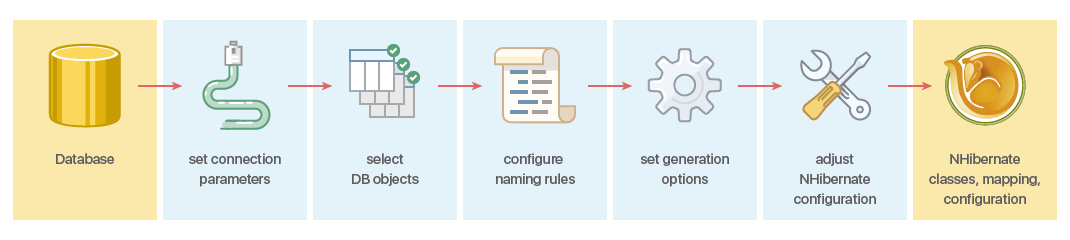
Entity Developer for NHibernate offers advanced NHibernate generator functionality for generating NHibernate entity code and NHibernate mapping. To generate entity code and mapping from a database, you need to perform several simple steps, described below.
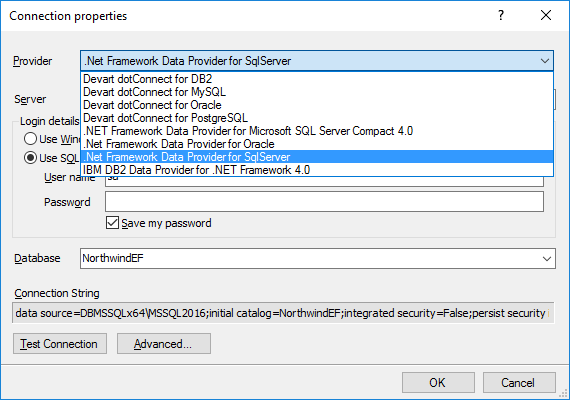
1. Connecting to a Database
To connect to a database you need to specify the provider and the connection settings. Entity Developer for NHibernate supports any third-party ADO.NET data providers for SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQLite. When using Entity Developer integrated to Visual Studio, Entity Developer supports provider-specific connection dialogs to specify the connection settings.
2. Selecting Objects
Entity Developer allows you to select tables and views for generating entities. Tables and views are grouped into the corresponding nodes. You may choose whether to view objects from all the schemas or only from the current one, specified in the connection. In case you are selecting objects from multiple schemas, you may ease the selecting of the database objects by enabling grouping objects by schemas.
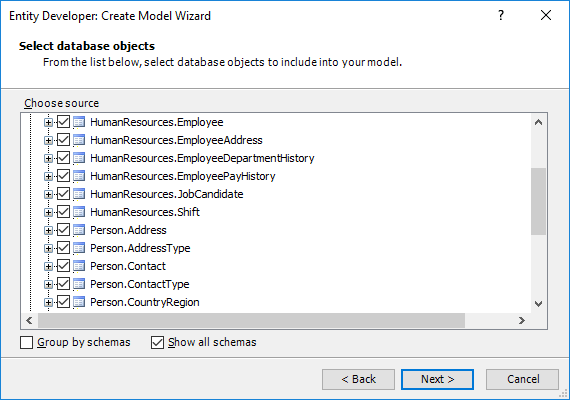
3. Setting Naming Rules
Entity Developer allows flexible tweaking naming rules for the generated names of the classes and their members. Entity Developer allows you to configure case and pluralization, removing and adding of prefixes and suffixes, add the schema name as the prefix, remove underscores from the database object names, etc. You may immediately view how the names are changed on a sample name.
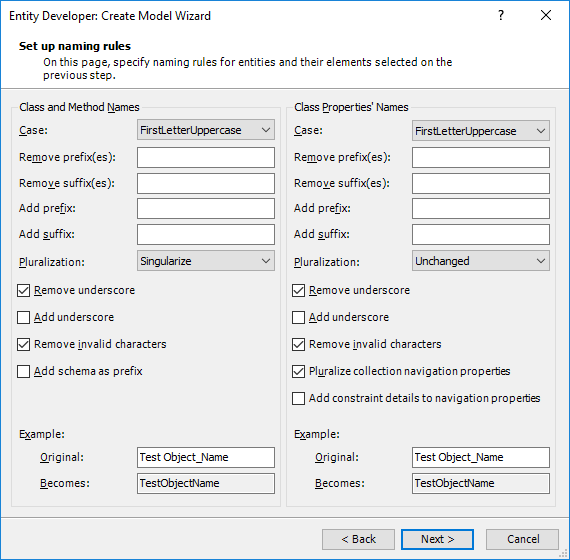
4. Tweaking Model Settings
On this step you can set the default parameters for the generated classes: default assembly and namespace, default schema, cascade style, strategy for accessing a property value, default identity generator and its parameters, etc. You can also enable or disable automatic detection of many-to-many associations and TPT inheritances.
Entity Developer allows you to generate mapping containing all the schema details or preserve only the cross-database schema information to create database-independent models. Alternatively you may disable storing the database schema information in the mapping.
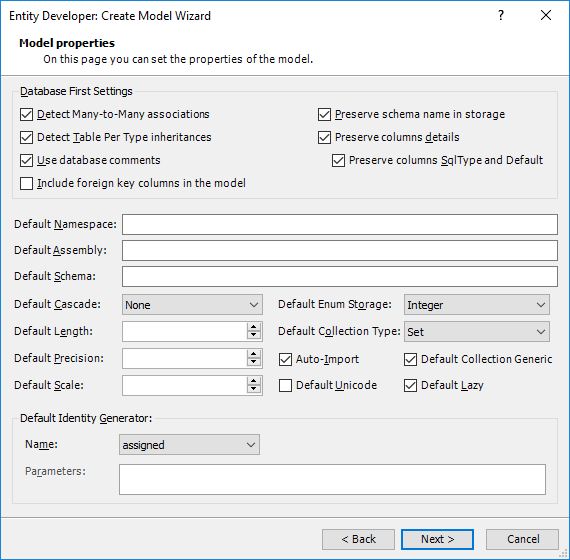
5.Customizing Generation
Entities Generation
In the generation settings you may perform additional tweaking of the generation of NHibernate entities and mapping. Entity Developer offers a number of settings to configure different aspects of entity generation:
Well-known Interface Implementation
Generate classes with or without Equals and GetHashCode implementation, IValidatable interface implementation, and support for IPropertyChanging and IPropertyChanged events.
-
WCF Support
Set the Generate Data Contract Attribute property for entity classes and the Generate Data Member Attribute property for entity properties - for all model entities and properties together or for each one separately.
-
Custom .NET Attribute Support
Easily assign attributes from available assemblies to classes, properties or contexts of a model.
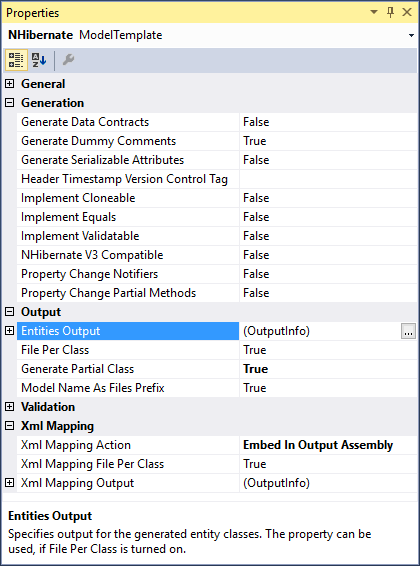
Mapping Generation
As for generating NHibernate mapping, Entity Developer can generate XML, Fluent NHibernate, and Loquacious (Mapping by code) mapping.
For XML mapping you may customize output settings, use the File per class option. XML mapping is generated as an embedded resource by default, however you may change this behaviour and generate mapping as separate XML files.
Entity Developer provides full support for Fluent NHibernate mapping - it supports all kinds of inheritances, components, composite IDs, etc.
Configuration Generation
Entity Developer for NHibernate is also capable to generate NHibernate configuration XML code. You may tweak the NHibernate configuration settings in the Model Settings dialog box and then generate the configuration code either to the App.config file of the project or to a separate *.cfg.xml file.